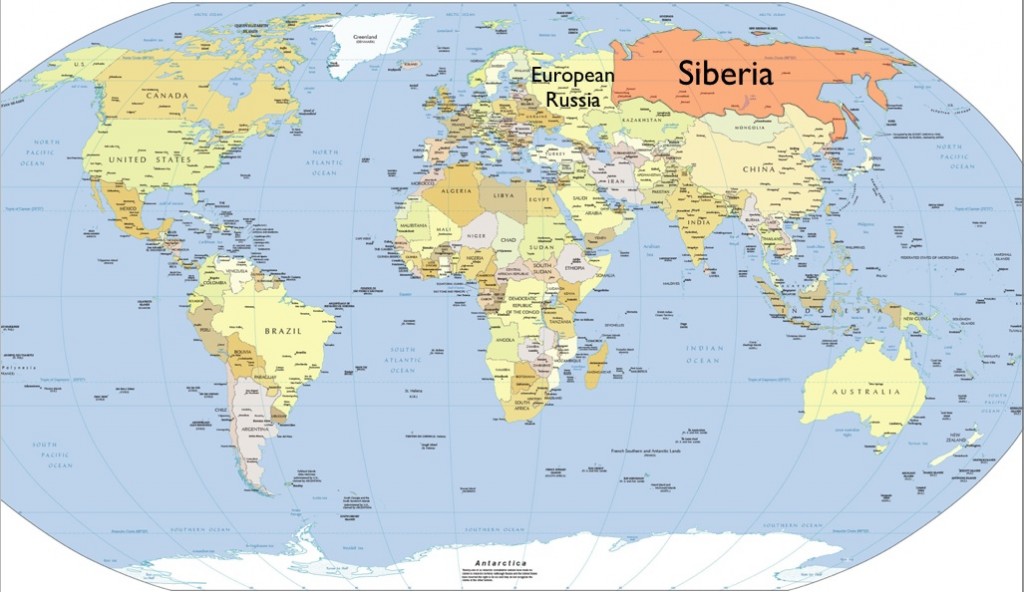
Siberia location is one of the most mysterious and intriguing places on Earth. Stretching across a staggering expanse of land in northern Asia, this region has fascinated explorers, scientists, and adventurers for centuries. Its unique geography, harsh climate, and rich cultural history make it a truly remarkable destination. If you're curious about Siberia, you've come to the right place.
Siberia occupies approximately 77% of Russia's total land area and is home to some of the world's most diverse ecosystems. From frozen tundras to dense forests, the region's natural beauty is unmatched. This article will delve into the geography, climate, history, and culture of Siberia, offering a comprehensive overview of this fascinating part of the world.
Whether you're planning a trip to Siberia or simply want to learn more about its unique location, this article will provide all the information you need. Let's explore Siberia together and uncover what makes this region so special.
Read also:Palisades Mall Movie Theater A Comprehensive Guide To The Ultimate Movie Experience
Understanding the Geography of Siberia Location
Siberia's location is defined by its vast expanse of land that stretches from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. This region covers an area of over 13 million square kilometers, making it one of the largest landmasses in the world.
Key Geographic Features of Siberia
Siberia is home to several key geographic features that define its landscape:
- Mountains: The Ural Mountains mark the western boundary of Siberia, while the Sayan and Altai ranges run through the southern part of the region.
- Rivers: Major rivers such as the Ob, Yenisei, and Lena flow through Siberia, providing vital water sources for the region's ecosystems.
- Forests: The taiga, or boreal forest, covers much of Siberia and is the largest forest biome in the world.
- Tundra: In the northernmost parts of Siberia, the frozen tundra dominates the landscape, supporting unique flora and fauna.
The Climate of Siberia Location
Siberia's climate is as diverse as its geography. The region experiences extreme temperature variations, with some of the coldest temperatures recorded on Earth.
Seasonal Changes in Siberia
The climate of Siberia can be divided into four distinct seasons:
- Winter: Lasting from November to March, winters in Siberia are notoriously harsh, with temperatures often dropping below -50°C (-58°F).
- Spring: From April to June, the snow begins to melt, and the land starts to awaken after the long winter.
- Summer: July to September sees relatively mild temperatures, with some areas experiencing warm weather suitable for outdoor activities.
- Autumn: October brings cooler temperatures and vibrant foliage, signaling the approach of another long winter.
A Brief History of Siberia Location
The history of Siberia is rich and complex, with evidence of human habitation dating back thousands of years. The region has been home to various indigenous groups, each contributing to its cultural diversity.
Indigenous Peoples of Siberia
Some of the indigenous peoples of Siberia include:
Read also:Jane Waldhorn Unveiling The Extraordinary Life And Legacy
- Yakuts: Known for their horse breeding and reindeer herding, the Yakuts are one of the largest indigenous groups in Siberia.
- Evenks: Nomadic hunters and reindeer herders, the Evenks have adapted to Siberia's harsh environment over centuries.
- Chukchi: Living in the northeastern part of Siberia, the Chukchi are known for their reindeer herding and traditional hunting practices.
Siberia Location in Modern Times
Today, Siberia plays a vital role in the global economy, particularly in the areas of energy and natural resources. The region is rich in oil, gas, and minerals, making it a key player in international trade.
Economic Importance of Siberia
Siberia's economic significance can be seen in several industries:
- Energy: Siberia is home to some of the largest oil and gas reserves in the world, supplying energy to countries across Asia and Europe.
- Minerals: The region is rich in precious metals and gemstones, including gold, diamonds, and platinum.
- Agriculture: Despite its harsh climate, parts of Siberia are suitable for farming, particularly in the southern regions.
Exploring the Cultural Heritage of Siberia Location
Siberia's cultural heritage is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of its people. From traditional crafts to modern art, the region's cultural landscape is as diverse as its geography.
Traditional Crafts of Siberia
Some of the traditional crafts of Siberia include:
- Wood Carving: Intricately carved wooden items are a hallmark of Siberian craftsmanship.
- Fur Clothing: The use of animal furs for clothing is a practical and traditional aspect of Siberian life.
- Musical Instruments: Unique instruments such as the khomus (a type of jaw harp) are still played by indigenous groups today.
The Wildlife of Siberia Location
Siberia is home to a wide variety of wildlife, adapted to survive in its harsh conditions. From the Siberian tiger to the Arctic fox, the region's fauna is both diverse and fascinating.
Key Species of Siberia
Some of the key species found in Siberia include:
- Siberian Tiger: One of the largest cat species in the world, the Siberian tiger is native to the forests of eastern Siberia.
- Reindeer: A vital part of the diet and culture of many indigenous groups, reindeer are well-adapted to the cold climate.
- Arctic Fox: With its thick fur and ability to survive in extreme cold, the Arctic fox is a symbol of Siberia's resilience.
Travel and Tourism in Siberia Location
For adventurous travelers, Siberia offers a wealth of opportunities to explore its natural beauty and cultural heritage. From the Trans-Siberian Railway to Lake Baikal, the region is full of attractions that are sure to captivate visitors.
Top Attractions in Siberia
Some of the top attractions in Siberia include:
- Trans-Siberian Railway: The longest railway in the world, the Trans-Siberian Railway offers a unique way to experience Siberia's vastness.
- Lake Baikal: Known as the deepest and oldest lake in the world, Lake Baikal is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a must-visit destination.
- Novosibirsk: As the largest city in Siberia, Novosibirsk is a hub of culture, science, and industry.
Siberia Location and Global Warming
The effects of global warming are becoming increasingly apparent in Siberia, with rising temperatures and melting permafrost posing significant challenges to the region's ecosystems and infrastructure.
Impact of Climate Change on Siberia
Some of the impacts of climate change on Siberia include:
- Permafrost Melting: The thawing of permafrost is releasing greenhouse gases and destabilizing infrastructure.
- Wildfires: Increased temperatures have led to more frequent and severe wildfires in the region.
- Animal Migration: Changes in climate are causing some species to migrate to new areas in search of suitable habitats.
Conclusion: Why Siberia Location Matters
Siberia's location is more than just a geographical designation; it is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of both its people and its ecosystems. From its rich history and cultural heritage to its vast natural resources and unique wildlife, Siberia offers a wealth of knowledge and experience for those willing to explore it.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences about Siberia in the comments below. Whether you've visited the region or simply appreciate its beauty and significance, your input is valuable. Don't forget to explore other articles on our site for more insights into the world's most fascinating destinations.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Geography of Siberia Location
- The Climate of Siberia Location
- A Brief History of Siberia Location
- Siberia Location in Modern Times
- Exploring the Cultural Heritage of Siberia Location
- The Wildlife of Siberia Location
- Travel and Tourism in Siberia Location
- Siberia Location and Global Warming
- Conclusion: Why Siberia Location Matters