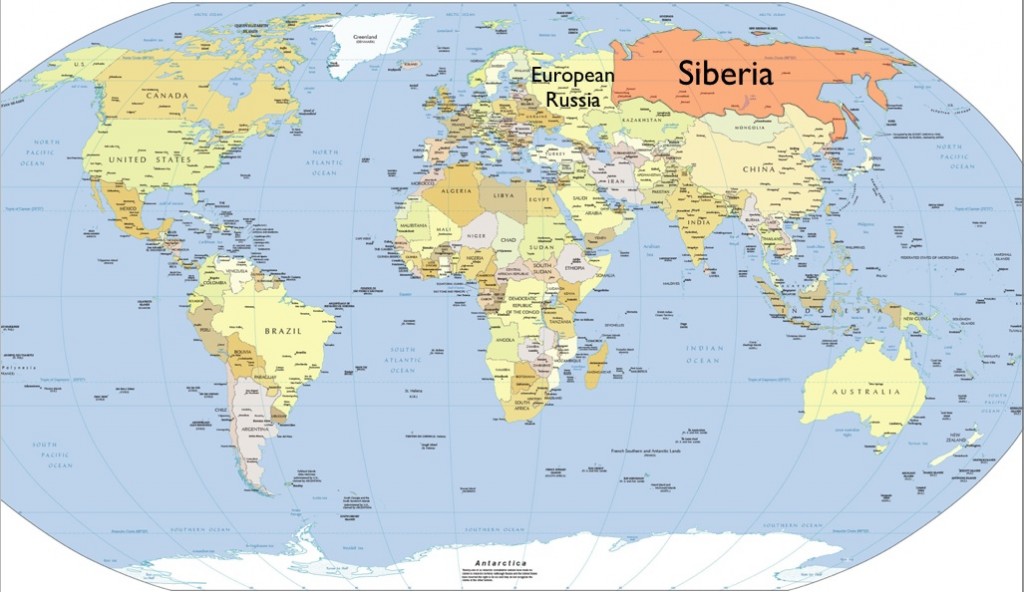
When people hear the name "Siberia," they often think of a vast, cold, and remote region of Russia. But where is Siberia located exactly? This article will explore the geographical, historical, and cultural aspects of Siberia to provide a complete understanding of its significance on the global map.
Siberia is a massive territory that stretches across much of northern Asia, encompassing diverse landscapes from frozen tundras to dense forests and sprawling plains. Its strategic location makes it an integral part of Russia and plays a vital role in the country's economy, politics, and culture.
In this article, we will delve into the geographical positioning of Siberia, its unique characteristics, and its importance in the modern world. Whether you're a geography enthusiast or simply curious about this enigmatic region, this guide will provide all the information you need to understand where Siberia is located and why it matters.
Read also:Eva Artificial Intelligence Revolutionizing The Future Of Ai
Table of Contents
- Geographical Overview of Siberia
- Siberia's Location and Boundaries
- Physical Features of Siberia
- Climate in Siberia
- Historical Background of Siberia
- Siberia's Economy
- Population and Demographics
- Cultural Significance of Siberia
- Environmental Issues in Siberia
- Why is Siberia Important?
Geographical Overview of Siberia
Siberia is one of the most extensive regions in the world, covering approximately 13.1 million square kilometers, which accounts for about 77% of Russia's total land area. The region extends from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east, making it a vital part of Asia's geography.
Geographically, Siberia is divided into three main zones: the Western Siberian Plain, the Central Siberian Plateau, and the Eastern Siberian Mountains. These zones contribute to the region's diverse topography, which includes rivers, lakes, forests, and mountains.
Siberia's Location and Boundaries
Where is Siberia located? Siberia is situated in northern Asia, spanning from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. Its northern boundary is marked by the Arctic Ocean, while its southern border touches Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and China.
- Western Boundary: Ural Mountains
- Eastern Boundary: Pacific Ocean
- Northern Boundary: Arctic Ocean
- Southern Boundary: Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and China
These boundaries define Siberia as a vast and expansive region that plays a crucial role in Russia's geopolitical landscape.
Physical Features of Siberia
Siberia is known for its dramatic and varied physical features, which include mountains, plains, rivers, and forests. The region is home to some of the world's largest and most significant natural landmarks.
Mountains and Plateaus
The Central Siberian Plateau and the Eastern Siberian Mountains are two of the most prominent geological features of the region. The plateau covers a significant portion of Siberia and is characterized by its elevated terrain and rugged landscape.
Read also:Vince Young Steakhouse In Austin A Culinary Gem With A Legacy
In contrast, the Eastern Siberian Mountains are a series of mountain ranges that stretch across the eastern part of the region. These mountains contribute to the region's biodiversity and offer opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking and skiing.
Climate in Siberia
Siberia is notorious for its harsh climate, with temperatures that can plummet to -68°C (-89°F) during the winter months. The region experiences a subarctic climate, which is characterized by long, cold winters and short, mild summers.
Despite the harsh conditions, Siberia's climate supports a wide range of flora and fauna, including species that have adapted to survive in extreme temperatures. The region's climate also plays a significant role in shaping its economy and way of life.
Historical Background of Siberia
Siberia has a rich and complex history that dates back thousands of years. The region was originally inhabited by nomadic tribes, who were later conquered by various empires and civilizations.
In the 16th century, Siberia became part of the Russian Empire after a series of military campaigns led by Russian explorers and settlers. The region played a crucial role in the expansion of Russia's territory and contributed significantly to the country's economic and political development.
Siberia's Economy
Siberia is a vital economic hub for Russia, thanks to its abundant natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals. The region is home to some of the world's largest oil and gas reserves, making it a key player in the global energy market.
Additionally, Siberia's vast forests and fertile plains support a thriving agricultural industry, while its rivers and lakes provide opportunities for fishing and aquaculture. The region's economy is diverse and continues to grow, contributing significantly to Russia's GDP.
Population and Demographics
Siberia's population is relatively small compared to its vast size, with approximately 36 million people living in the region. The population is predominantly Russian, with smaller ethnic groups such as the Tatars, Yakuts, and Buryats also calling Siberia home.
The region's harsh climate and remote location have historically deterred large-scale settlement, resulting in a sparse and scattered population. However, recent developments in infrastructure and technology have made Siberia more accessible and attractive to new residents.
Cultural Significance of Siberia
Siberia has a rich cultural heritage that reflects its diverse population and history. The region is home to numerous indigenous groups, each with its own unique traditions, languages, and customs.
Siberian culture is characterized by its strong connection to nature and the environment, as well as its rich folklore and storytelling traditions. The region's cultural significance extends beyond its borders, influencing Russian culture and art on a national and global scale.
Environmental Issues in Siberia
Despite its natural beauty and resources, Siberia faces several environmental challenges, including deforestation, pollution, and climate change. These issues threaten the region's biodiversity and the livelihoods of its inhabitants.
Efforts are being made to address these challenges through conservation programs and sustainable development initiatives. The Russian government and international organizations are working together to protect Siberia's fragile ecosystems and ensure their preservation for future generations.
Why is Siberia Important?
Siberia is an important region for several reasons, including its strategic location, abundant natural resources, and cultural significance. The region plays a vital role in Russia's economy and politics, as well as in global environmental and energy discussions.
Understanding where Siberia is located and its importance is essential for anyone interested in geography, history, or global affairs. By exploring the region's geography, history, and culture, we can gain a deeper appreciation for its significance and the challenges it faces.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Siberia is a vast and fascinating region that plays a crucial role in Russia's economy, politics, and culture. Its strategic location, abundant natural resources, and rich cultural heritage make it an important part of the global landscape.
By understanding where Siberia is located and its significance, we can appreciate the challenges and opportunities it presents. We encourage readers to share this article, leave comments, and explore other articles on our site to learn more about this remarkable region.
References:
- World Bank. (2022). "Siberia's Economic Development."
- UNESCO. (2021). "Cultural Heritage of Siberia."
- National Geographic. (2020). "Environmental Challenges in Siberia."